Tinnitus is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide (1 in 7, according to recent research), causing persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the ears. While it can be a minor nuisance for some, for others, it significantly impacts their quality of life. Whether you’re experiencing mild or severe tinnitus, understanding the condition is the first step towards effective management and relief.
In this blog, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and types of tinnitus, explain the diagnostic process, and provide practical tips for tinnitus treatment. With the right knowledge and tools, you can take control of your tinnitus and improve your overall quality of life.
In This Article:
What Is Tinnitus?
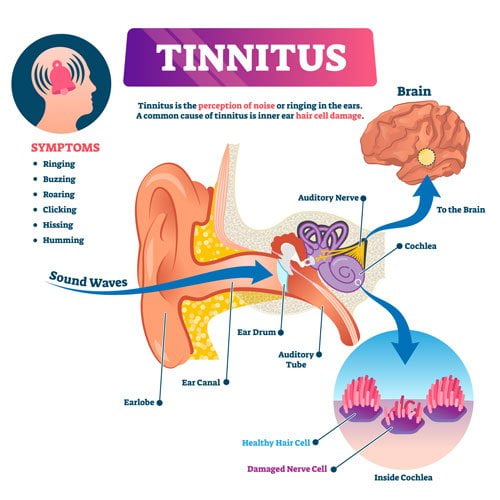
Tinnitus is a condition characterised by the perception of noise or ringing in the ears in the absence of any external sound. This phenomenon occurs when the auditory system, which includes the ear, the auditory nerve connecting the inner ear to the brain, and parts of the brain that process sound, generates signals that are interpreted as sound. These phantom sounds can be continuous or intermittent and can vary greatly in pitch, loudness, and type.
1) Common Symptoms
- Ringing: A high-pitched ringing sound is the most commonly reported symptom.
- Buzzing: Some people experience a low or high buzzing noise.
- Hissing: A hissing or static-like sound is another common symptom.
- Humming: A low, continuous hum can also be a sign of tinnitus.
- Roaring: A sound similar to the ocean waves or a roaring engine.
- Clicking: Rhythmic clicking noises that may be in time with your heartbeat.
These sounds can be constant or intermittent and can vary in loudness. They might be more noticeable in quiet environments or at night when background noise is minimal.
2) Types of Tinnitus
- Subjective: This is the most common type (approximately 95% of the cases), where only the person experiencing it can hear the sounds. It can be caused by problems in the outer, middle, or inner ear, as well as issues with the auditory nerves or the part of the brain that interprets nerve signals as sound.
- Objective: This type is rare (about 5% of the cases) and can be heard by both the affected person and the doctor conducting the examination. It’s often caused by physical issues such as a vascular problem, a muscle contraction, or a bone condition in the middle ear.
Understanding the basics of the condition is the first step in managing and treating it effectively. In the following sections, we’ll explore the various causes, diagnosis methods, and treatment options available to help you find relief.
Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can be triggered by a variety of factors, ranging from hearing loss to medical conditions. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for management and treatment. Here are some of the most common causes:
1) Hearing Loss and Tinnitus
As people age, the delicate hair cells in the inner ear can become damaged or die, leading to hearing loss and often, tinnitus. This condition is known as presbycusis. When it occurs, the damaged cells may start sending random electrical impulses to the brain, leading to the perception of sound.
2) Noise Exposure
Loud noises from concerts, industrial environments, construction sites, or even listening to music at high volumes through headphones can damage the hair cells in the middle ear. This damage can result in temporary or permanent tinnitus. To prevent this, it’s important to use hearing protection in noisy environments.
3) Ear Infections and Earwax Blockage
Ear infections can lead to inflammation and fluid build-up in the middle ear, which can interfere with hearing and cause tinnitus. Similarly, excessive earwax can block the ear canal, preventing sound waves form reaching the inner ear. This blockage can alter the pressure in the ear and lead to tinnitus.
4) Medications and Tinnitus
Certain medications can cause or worsen this condition as a side effect. These medications include some antibiotics, diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and chemotherapy drugs. Tinnitus caused by medication is often cause-dependent and may improve once the medication is discontinued or the dosage is adjusted. If you suspect that your medication is causing tinnitus, consult your doctor for possible alternatives or adjustments.
5) Other Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can cause or contribute to the condition:
- Meniere’s Disease: A disorder of the inner ear that affects balance and hearing.
- Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMJ) Disorders: Problems with the joint that connects your jaw to your skull.
- Acoustic Neuroma: A benign tumour on the cranial nerve that affects hearing and balance.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Conditions like high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and abnormal blood flow can cause pulsatile tinnitus, which is characterised by a rhythmic sound that often matches the heartbeat.
- Thyroid Problems: Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can also cause tinnitus.
Understanding the causes of your condition can help guide treatment and management strategies. In the following sections, we’ll explore how tinnitus is diagnosed and the various treatment options available.
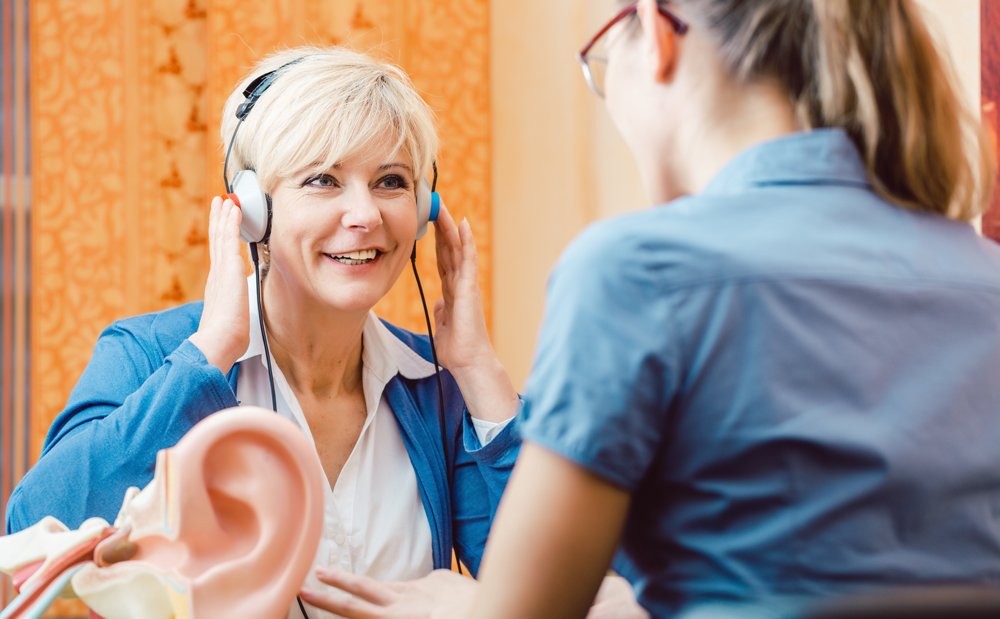
Diagnosing Tinnitus
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and management. Here’s what you need to know about when to seek medical advice and the diagnostic procedures involved:
1) When to See a Doctor
If you notice persistent ringing or noises in your ears that bother you or are accompanied by other symptoms, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare professional. You should seek medical advice as soon as possible if:
- It starts suddenly or without an apparent cause.
- You hear the noise in only one ear.
- You experience dizziness, balance issues, or ear pain.
- There is ear discharge or a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Early diagnosis can help point out any underlying conditions causing the issue and improve your chances of finding effective treatment.
2) Hearing Tests
The first step of the diagnosis process typically involves a thorough hearing evaluation by an audiologist or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. Common tests include:
- Audiometry: This test measures your hearing sensitivity across different frequencies and volumes. You’ll wear headphones and indicate when you hear sounds, helping to determine if hearing loss is present.
- Tympanometry: This test evaluates the function of your middle ear by measuring the movement of the eardrum in response to changes in air pressure. It helps detect issues such as fluid build-up or eardrum perforations.
- Speech Recognition Test: These tests assess your ability to hear and understand speech at different volume levels and in various noise environments.
3) Imaging Tests and Other Diagnostic Procedures
Sometimes, additional tests are needed to get to the root of the problem. These might include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Using magnets and radio waves, an MRI creates detailed images of your brain and inner ear structures. It’s helpful for ruling out tumours or other abnormalities.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan takes X-ray images from different angles to create detailed cross-sectional images of your head and ear structures, which can help spot issues like bone abnormalities or tumours.
- Blood Tests: These can check for underlying conditions like thyroid problems, anaemia, or infections that might be contributing to the problem.
- Balance Tests: If you’re experiencing dizziness of balance issues along with tinnitus, balance tests can assess how well your inner ear is working.
These diagnostic steps help healthcare professionals understand what’s causing your tinnitus and how best to treat it. Up next, we’ll look at how tinnitus affects daily life and explore the various treatment options available to help you find relief.

Impact of Tinnitus on Daily Life
Tinnitus isn’t just a nuisance; it can significantly impact your daily life in many ways. Let’s take a closer look at how it can affect you emotionally, psychologically, and physically.
1) Emotional and Psychological Effects
Living with tinnitus can be challenging. The constant ringing or buzzing in your ears can lead to a range of emotional and psychological effects, including:
- Stress and Anxiety: The persistent noise can be stressful and make you feel anxious. It’s natural to worry about the noise never going away, which can heighten anxiety levels.
- Frustration and Irritability: When you can’t escape the noise, it can be incredibly frustrating. This can make you feel irritable, or cause mood swings.
- Depression: In some cases, the constant noise and its impact on your life can contribute to feelings of depression. It’s important to seek support if you’re feeling this way.
2) Impact on Sleep and Concentration
The condition can also interfere with your ability to sleep and concentrate, which are crucial for your overall wellbeing and productivity.
- Sleep Disruption: The constant noise can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. This can leave you tired and less able to cope with the noise during the day.
- Difficulty Concentrating: The intrusive noise can make it harder to focus on tasks, especially those that require a lot of attention. This can affect your performance at work or school and make daily activities more challenging.
- Cognitive Effects: Tinnitus is sometimes linked to cognitive fatigue, as in some people, it makes it harder to process information and think clearly.
It’s crucial to talk to a healthcare provider about your tinnitus and its impact on your mental health. There are various therapies and support groups available that can help you manage the emotional and psychological effects.
Managing Tinnitus
Dealing with tinnitus can be tough, but there are several ways to manage it and improve your quality of life. Here are some practical tips and strategies that can help:
1) Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Simple changes to your daily routine can make a big difference in managing tinnitus.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress and improve your overall wellbeing, which can lessen the impact of tinnitus.
- Avoid Loud Noises: Protect your ears from loud environments by using earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones. Avoiding loud noises can prevent your tinnitus from getting worse.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can exacerbate tinnitus for some people. If you’re a regular consumer of those, try reducing your intake to see if it helps.
2) Sound Therapy and Masking Devices
Sound therapy uses external noise to alter your perception of or reaction to tinnitus.
- White Noise Machines: These devices produce a consistent sound that can help mask the tinnitus, making it less noticeable.
- Hearing Aids: For those with hearing loss and tinnitus, hearing aids can amplify external sounds, which can help mask the tinnitus.
- Sound Masking Devices: These small electronic devices usually come in the form of specialised earphones and are designed to produce a soft, pleasant sound that takes your attention off the tinnitus.
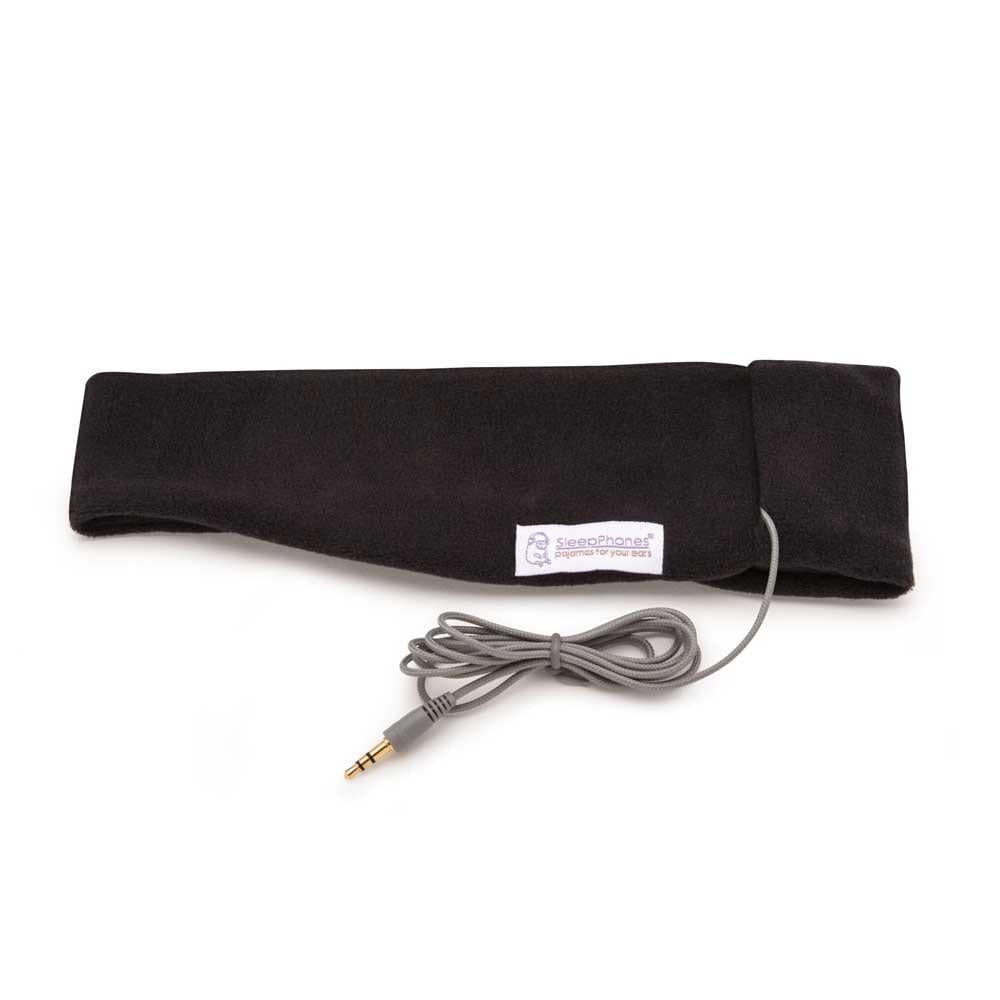
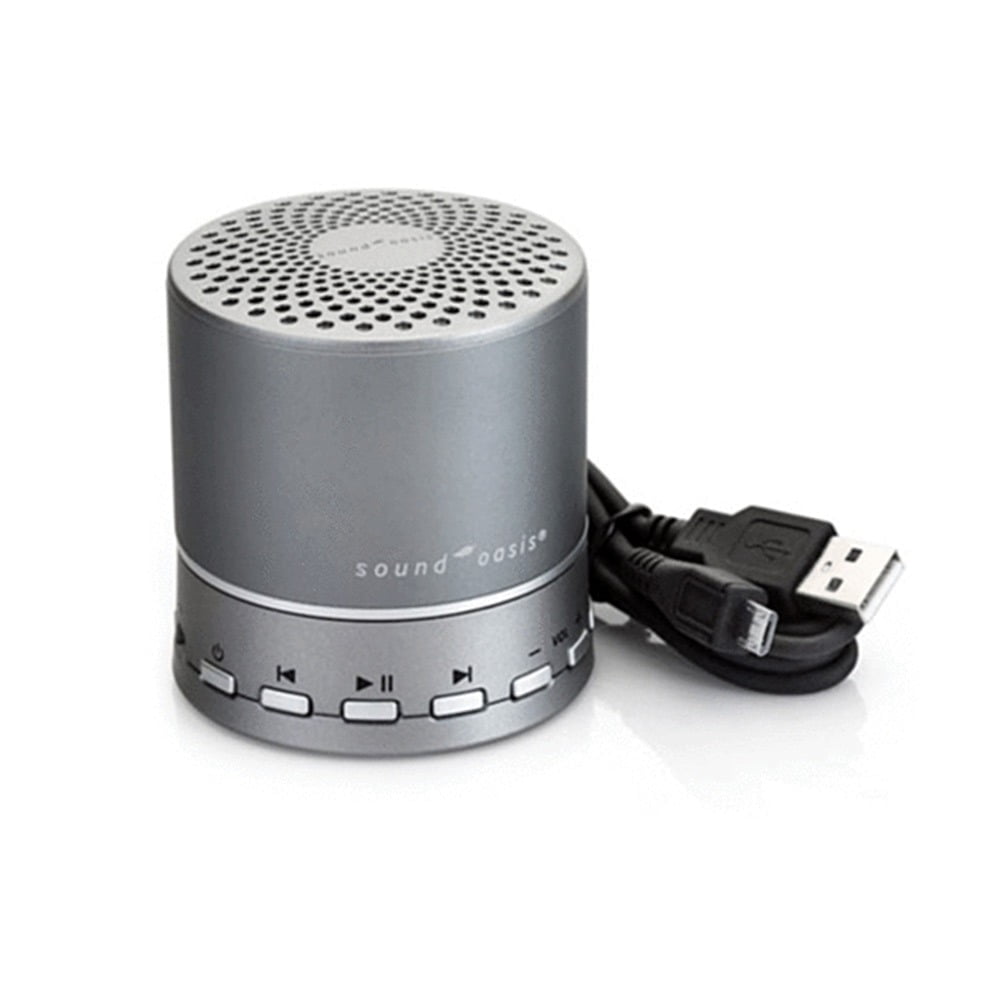
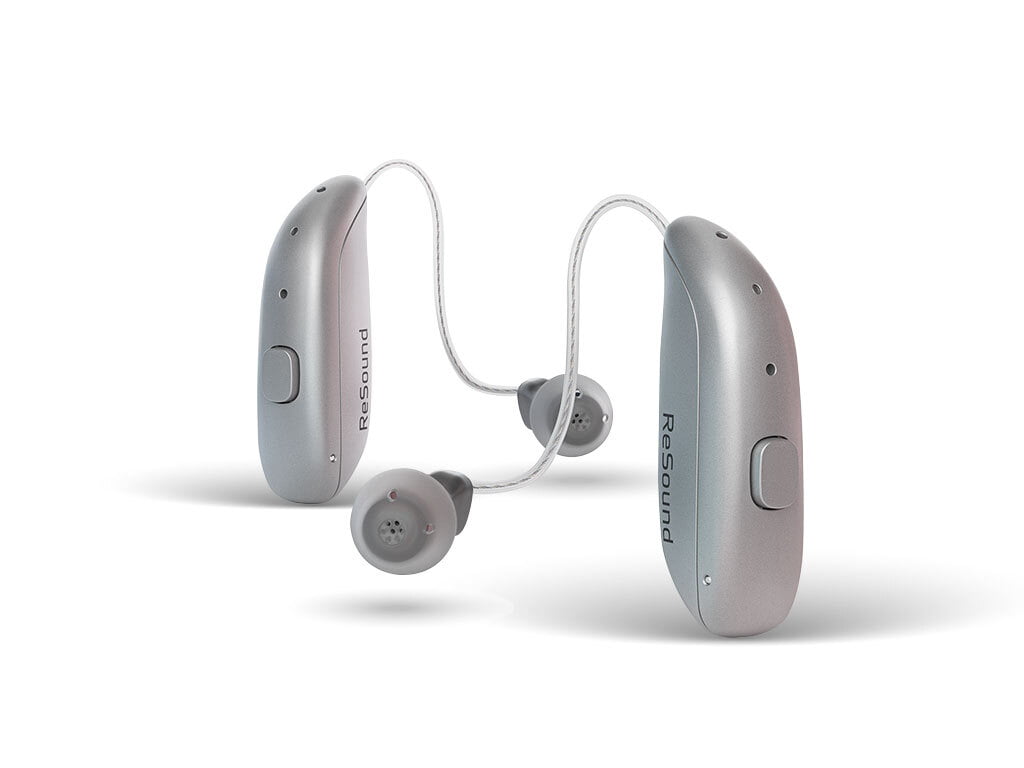




3) Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
Stress can make the perceived noise worse, so finding ways to manage it is crucial.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help you focus on the present moment and reduce stress, which can lessen the impact of tinnitus symptoms.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing can help calm your nervous system and reduce stress. Try taking slow, deep breaths when you feel overwhelmed.
- Yoga: This gentle physical activity combines movement and meditation, helping you relax and reduce stress.
4) Dietary Considerations
What you eat can also affect your tinnitus.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep your body functioning well.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a healthy, balanced diet can improve your overall health, which may help reduce symptoms. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Some foods, for example those that contain high levels of sodium, can make your symptoms worse. Pay attention to what you eat and see if certain foods trigger your tinnitus.
Managing tinnitus is a journey, and what works for one person might not work for another. It’s about finding the right combination of strategies that work for you. In the next section, we’ll look at professional treatment options that can provide additional support and relief.
Treatment Options for Tinnitus
If lifestyle changes and home remedies aren’t enough, there are several professional treatment options available that can provide relief. Let’s explore some of the most effective treatments:
1) Hearing Aids
For many people with tinnitus, especially those with hearing loss, hearing aids can be incredibly beneficial. They can help amplify external sounds, making the tinnitus less noticeable. Furthermore, some hearing aids come with built-in tinnitus masking features, producing soothing sounds that help mask the tinnitus.
2) Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a type of counselling that can help you manage tinnitus by changing the way you think about it. It helps you identify and change negative thought patterns related to tinnitus, reducing stress and anxiety. It can also help you learn techniques to cope with tinnitus, making it less intrusive and easier to live with.
3) Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT)
TRT combines sound therapy with counselling to help you become less aware of your tinnitus. It uses low-level background noise to reduce the perception of tinnitus. Additionally, it helps you understand your condition better and develop coping strategies, aiming to habituate you to the sound so it becomes less bothersome.
4) Medications and Supplements
While there is no specific medication for tinnitus, some drugs and supplements can help manage the symptoms.
- Medications: Anti-anxiety medications, antidepressants, and other drugs can sometimes help reduce the severity of tinnitus symptoms.
- Supplements: Some people find relief with supplements such as ginkgo biloba, zinc, and magnesium, though their effectiveness can vary.
5) Surgical Options
Surgery is rarely used to treat tinnitus, but it may be an option in certain cases. For example, if tinnitus is caused by a specific medical condition, such as a tumour or vascular issue, surgery to correct the condition may alleviate the tinnitus. However, surgery is usually considered a last resort and is only recommended in cases where other treatments have not been effective.
Exploring these treatment options with your healthcare provider can help you find the most effective way to manage your tinnitus. Remember, what works for one person might not work for another, so it may take some time to find the right treatment plan for you.
Conclusion
Living with tinnitus can be challenging, but with the right knowledge, coping strategies, and support, you can manage the condition effectively and maintain a high quality of life. Understanding what tinnitus is, its causes, and the available treatments can empower you to take control of your symptoms.
If you’re experiencing tinnitus, remember that you’re not alone and there are many resources and treatments available to help you. From lifestyle changes and sound therapy to professional treatments like CBT and hearing aids, there are various ways to reduce the impact of tinnitus on your daily life.
It’s important to remember that tinnitus can sometimes be a sign of hearing loss. If you’re experiencing tinnitus, it’s a good idea to get your hearing checked. At Hear4U, we offer free, comprehensive hearing tests to help identify any underlying issues and provide you with the best solutions to manage your hearing health.
Take the first step towards better hearing and tinnitus management. Click the button below to book your free hearing test with Hear4U today.






